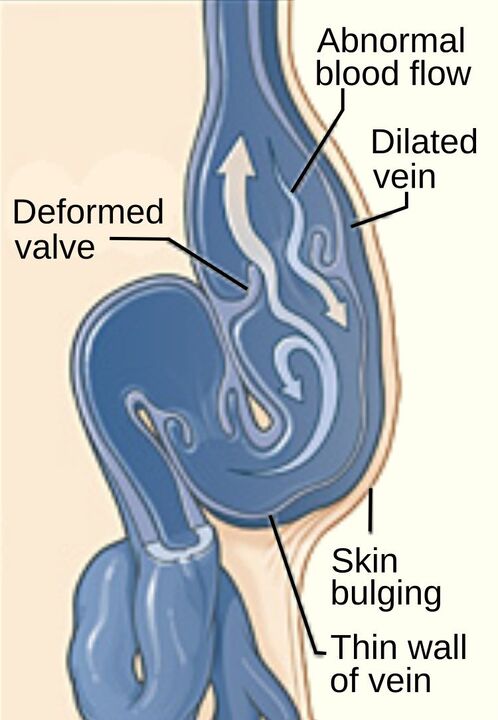
Varicose veins of the legs (varicose veins) are a common disease, manifested by persistent and irreversible dilation and lengthening of the superficial veins and disruption of their function due to the development ofof a pathological process in the walls of the veins and congenital or acquired valve insufficiency of the apparatus.
According to the World Health Organization, varicose veins are found in every fifth adult on the planet. The first signs of varicose veins (venous reflux) are detected in 10-15% of children and adolescents aged 12-13 years.
Causes of varicose veins in the legs
- Genetic predisposition (congenital weakness of vascular valves). If your parents have signs of weakening of the walls of veins in any vessels (legs, groin, esophagus, rectum), then there is a high probability that symptoms of varicose veins may appear in you.
- Poor circulation in the lower limbs during pregnancy and childbirth (the developing fetus compresses the abdominal veins with increased pressure in the veins of the legs, hormonal changes reduce the tone of the veins).
- Blood flow is obstructed when standing for long periods of time (varicose veins of the lower extremities are more common in salespeople, teachers, waiters, surgeons) and in a sitting position (managers, accountants, office workers). room, driver, etc. )
- Heavy physical work, sports training involving weight lifting (for athletes, movers, construction workers, people who regularly visit gyms and fitness clubs)
- Long-term use of birth control pills with high levels of female sex hormones.
- Hormonal changes in the body, accompanied by a decrease in the tone of venous blood vessels (adolescence, pregnancy, menopausal disorders in old age).
- Factors such as being overweight, chronic cough, constipation and wearing tight clothing and shoes disrupt the flow of veins and often lead to varicose veins.
Why do varicose veins occur during pregnancy?
In women, varicose veins of the lower limbs are observed 3-5 times more often than in men and occur quite often during pregnancy. In 80% of cases, varicose veins first develop on the left leg, then only on the right leg.
- The appearance of varicose veins is facilitated by hormonal changes in the woman's body during pregnancy, which reduce the elasticity of the vein walls, stretch them and turn into varicose veins. .
- In a pregnant woman's body, the amount of blood circulating increases significantly. Increased venous pressure leads to thinning of the vein walls and local dilation (varicose veins).
- The growing fetus causes a corresponding expansion of the uterus and difficulties in circulating blood from the lower limbs through the pelvic veins due to increased intra-abdominal pressure and mechanical compression of the veins.
- The increased body weight of pregnant women also negatively affects the flow of veins.
Varicose veins of the lower limbs: symptoms
Varicose veins develop quite slowly, going through many main stages in succession:
- At the first stage, violation of venous circulation is accompanied by the appearance of individual "spider veins", thinning of the skin, through which, during physical activity, the veins dilate under the skin. Twisted cord pattern begins to appear (usually in the popliteal fossa), with no complaints.
- In the second stage of varicose veins, there is a feeling of heaviness, fatigue in the lower limbs, swelling of the legs in the evening and after long walks, a feeling of "pins and needles" crawling along the legs, night cramps. The calf muscles, upon careful examination, reveal some dilated veins in the lower legs, and sometimes - in the feet and thighs.
- The third stage of varicose veins of the lower extremities is characterized by a pronounced swelling of the venous nodes mainly on the inner surface of the legs, the appearance of dark brown or brown spots on the thin, susceptible skin. damage of the legs and the development of ulcers. dermatitis with itching and rash. The swelling in the legs is getting worse, making walking difficult.
- The fourth stage of varicose veins is the presence of dilated lymph nodes on the feet, legs and thighs, the appearance of complications of the disease (chronic venous insufficiency with trophic ulcers, bleeding from varicose veins). lesions, the development of thrombophlebitis).
- Sometimes the fifth stage is also distinguished - there are all the symptoms characteristic of the fourth stage of varicose veins, with the process of spreading to the areas of the groin, buttocks, perineum, the presence of manytrophic ulcers, appearance of elephantiasis, frequent exacerbations of thrombophlebitis and onset of disability.
Complications of varicose veins
- Superficial thrombophlebitis.
- Bleeding when varicose veins rupture.
- Dermatitis, eczema.
- Nutritional ulcers.
- Deep vein thrombosis (phleboembolism) and post-thrombotic disease.
- Pulmonary embolism (PE).
- Lymphedema (elephant disease).
Diagnosis of varicose veins
It is based on a clinical examination, performing functional tests and conducting specific studies of the veins.
- Clinical examination (clarify complaints, take medical history, examine, palpate).
- Doppler ultrasound.
- Ultrasound angioscanning.
- Volume measurement.
- Ascending and descending phlebography.
- Radionuclide venography (radiophlebography).
- Computed tomography and MRI (CT venography, MR venography).
- Intravascular ultrasound examination.
- Thermometer.
Treatment of varicose veins of the lower limbs
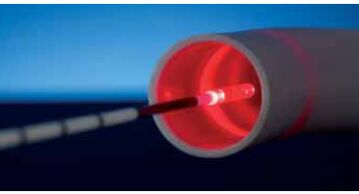
If varicose veins are detected in the early stages, you can cope with its manifestations using compression hosiery, special therapeutic exercises and traditional methods of treatment. But if you come to the doctor late, when the naked eye sees varicose veins, painful and swollen legs, trophic ulcers appear, signs of thrombophlebitis, then the only way out is surgical intervention.
At the same time, you should not be afraid of surgery, because modern technology makes it possible to eliminate varicose veins in the lower limbs without large incisions, without pain and practically without affecting a person's usual lifestyle.
The principles of surgical manipulation are similar for different techniques: pathologically altered superficial leg veins are ligated, excised, and excised. In this case, venous circulation in the lower extremities is not interrupted, since surgery does not affect the deep veins, where about 90% of venous blood flows.
Main types of surgery for varicose veins
- Sclerotherapy. In the early stages of varicose veins, a good cosmetic result is achieved by introducing special drugs into the problem veins, causing gradual hardening, "gluing" the area of pathological varicose veins. A medicinal substance (usually a sclerosing agent) is injected through a special catheter or very thin needle into the varicose vein. To achieve positive results, 3 to 10 injections are required.
- Removal of veins. An operation that has been performed for almost a hundred years, but in modern conditions, wide incisions have long been neglected. The operation today is performed through small incisions of 3-5 mm. Pathologically varicose veins are first ligated and transected at the point where they flow into the deep veins, then removed with special probes. This surgery lasts about 1-2 hours, after which the patient stays at the medical facility's hospital for 1-2 days.
- Removal of small veins. The surgery is performed under local anesthesia, without incisions but using small punctures to remove the varicose veins. This provides good cosmetic results (usually no stitches are needed) and significantly reduces post-operative recovery time. In some cases, it is not possible to remove the entire vein, but only its pathologically changed part. This intervention is called short stripping.
- Intravascular laser coagulation of venous blood. Manipulations are performed under ultrasound control. A special guided laser is inserted into the pathologically varicose vein and the saphenous vein and its branches are burned away. After a certain period of time, the veins become clogged and hardened, closing completely. If necessary, laser coagulation is combined with small vein ablation. In this case, the effectiveness of surgical treatment for lower limb varicose veins will be highest.
- Radiofrequency ablation of varicose veins. Removal ("gluing") of the lumen of the altered vein is achieved through exposure to radio waves of a certain power delivered to the problem area of the vein through a special catheter. The duration of the procedure is about 20 minutes.
After surgical treatment of varicose veins using one of the above methods, it is necessary to limit physical activity for a certain period of time, wear compression stockings and, if necessary, use drugs that have a varicose effect. This will help restore normal blood circulation in the veins of the lower limbs as soon as possible, prevent possible complications and allow you to quickly return to work and the normal rhythm of life.
In what cases is surgery to treat varicose veins in the legs undesirable?
- During pregnancy and in the first two months after birth.
- In the early stages of varicose veins, when there are no complaints yet and cosmetic problems ("spider veins" on the legs) are present, you can first try to get rid of them with group therapyeducation, compression hosiery and traditional methods.
- In old age and with serious diseases of dysfunction of various organs and systems of the body, when the risk of complications can increase significantly.
- When there are lymphatic drainage disorders, infectious skin lesions in the lower limbs, thrombophlebitis, arteriovenous fistula.
With the correct selection of the most effective treatment method for varicose veins of the lower extremities in this particular case, the absence of contraindications and following the doctor's recommendations in the postoperative period, positive results ofSurgical intervention would be warranted.
Prevention of varicose veins of the lower limbs
Regime and diet
In most cases, compliance with a certain regimen of work and rest as well as nutrition will prevent the appearance of varicose veins. To do this you need:
- Avoid wearing clothing that obstructs venous blood flow.
- Avoid standing or sitting for long periods of time (take periodic breaks and do simple exercises).
- Avoid strenuous physical activity.
- Lead an active lifestyle (moderate active load - daily walking, swimming, cycling).
- Drink at least 1. 5-2 liters of fluid per day, your daily diet should include vegetables and fruits, wholemeal bread and cereals.
- Avoid visiting baths and saunas, and refuse to take hot baths.
- Take contrast baths (warm - cool) every day.
- Use comfortable shoes with low heels.
Antiplatelet therapy
An important component of preventive measures for varicose veins of the lower extremities is the use of drugs with antiplatelet effect, that is, preventing the formation of blood clots. Including:
- Acetylsalicylic acid and modern drugs containing it;
- Brain tonics of plant origin - plant extracts such as horse chestnut, hazelnut, and mountain arnica are more commonly used;
- Synthetic poison. By the way, varicose veins not only reduce the formation of thrombi, but also improve venous blood circulation, strengthen the vessel walls, preventing the appearance of dilated areas.
Compression vest
For many years, bandaging with elastic tubular bandages has been used successfully in the early stages of varicose veins (when spider veins appear). Special clothes are now being produced - compression knitwear, which allows you to choose the required size and choose the degree of compression depending on the severity of the changes. Wearing socks and tights initially puts pressure on the top of the ankle, then relieves the pressure and stimulates blood flow toward the heart. Venous blood vessels work more efficiently, thanks to which venous congestion is eliminated, swelling disappears and the formation of blood clots is prevented.
Exercise
Special exercises have been developed aimed at eliminating venous blood stagnation. The key to success here is the regular implementation of the complex. Let's look at some basic exercises that are recommended in the presence of risk factors for the development of varicose veins of the lower limbs and in the early stages of the disease:
- Lie on your back, placing your feet on pillows on a raised platform. Relax and stay in this position for a few minutes.
- "Bicycle" - lie on your back, raise your legs high, bend your knees. Perform pedaling simulation movements while riding a bicycle;
- "Pull" - lie on your back, raise your legs up and cross them, change the position of the legs (up - down) for 1 minute;
- Legs raised and bent at the knee joints. Bend and straighten your legs, imitating walking;
- Lie on your back, bend your left leg, bring your knee to your chest. Wrap your hands around your legs at the ankle joints and gradually straighten your legs, performing massage movements on the calf muscles. Repeat the exercise with the right leg;
- Stand with your feet together. Stand up on your tiptoes and lower down (if there are no complications, the exercise can be performed forcefully - with your heels touching the floor).
Timely initiation and correct implementation of preventive measures can prevent varicose veins of the lower extremities or minimize their manifestations.